
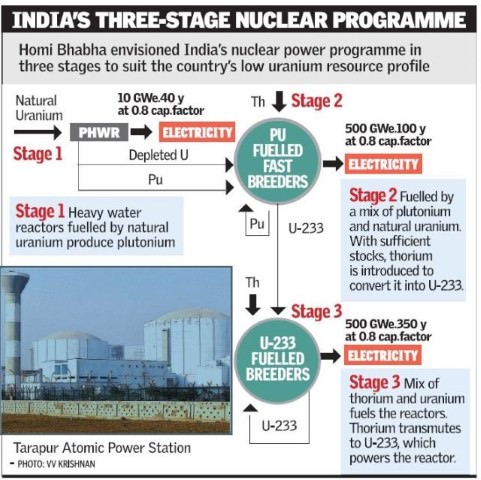
U-239 rapidly decays into Neptunium-239 which in turn rapidly decays into Plutonium-239. While exposed to the neutron flux during normal operation in the core environment a small percentage of the Uranium-238 in the fuel absorbs excess neutrons and is transmuted into U-239.
The thermal conductivity of uranium dioxide is very low compared with that of zirconium metal, and it goes down as the temperature goes up.Ĭorrosion of uranium dioxide in water is controlled by similar electrochemical processes to the galvanic corrosion of a metal surface. The aim is to form a dense solid which has few pores. The UO 2 is mixed with an organic binder and pressed into pellets, these pellets are then fired at a much higher temperature (in H 2/Ar) to sinter the solid. It can be made by heating uranyl nitrate to form UOģ UO 2 ( NO 3 ) 2 ⋅ 6 H 2 O ⟶ UO 3 + 2 NO 2 + 1 2 O 2 + 6 H 2 O ( g ) This is then heated (calcined) to form UOģ and U 3O 8 which is then converted by heating with hydrogen or ammonia to form UO 2. Uranium dioxide is a black semiconducting solid. The thermal conductivity of zirconium metal and uranium dioxide as a function of temperature Uranium dioxide 10.2 Radioisotope thermoelectric generatorįor fission reactors, the fuel (typically based on uranium) is usually based on the metal oxide the oxides are used rather than the metals themselves because the oxide melting point is much higher than that of the metal and because it cannot burn, being already in the oxidized state.9 Fuel behavior and post-irradiation examination.8.1 Oxide fuel under accident conditions.5 Common physical forms of nuclear fuel.Nuclear fuel has the highest energy density of all practical fuel sources. Not all types of nuclear fuels create power from nuclear fission plutonium-238 and some other elements are used to produce small amounts of nuclear power by radioactive decay in radioisotope thermoelectric generators and other types of atomic batteries. The processes involved in mining, refining, purifying, using, and disposing of nuclear fuel are collectively known as the nuclear fuel cycle. Alternatively, if the nucleus absorbs the neutron without splitting, it creates a heavier nucleus with one additional neutron.

This creates a self-sustaining chain reaction that is controlled in a nuclear reactor, or uncontrolled in a nuclear weapon. In that case, the neutrons released go on to split more nuclei. When the unstable nuclei of these atoms are hit by a slow-moving neutron, they frequently split, creating two daughter nuclei and two or three more neutrons. The three most relevant fissile isotopes are uranium-233, uranium-235 and plutonium-239. Most nuclear fuels contain heavy fissile actinide elements that are capable of undergoing and sustaining nuclear fission. Heat is created when nuclear fuel undergoes nuclear fission. Nuclear fuel is material used in nuclear power stations to produce heat to power turbines. Close-up of a replica of the core of the research reactor at the Institut Laue-Langevin


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
